Maintaining optimal health has become a priority for many in today’s fast-paced world, driving individuals to explore the essential nutrients that fuel our bodies. Magnesium stands out as a pivotal mineral critical for numerous bodily functions. This Magnesium guide offers an in-depth exploration into how magnesium contributes to our overall health and well-being. From supporting muscle and nerve function to aiding in producing energy and protein, magnesium is undeniably indispensable.
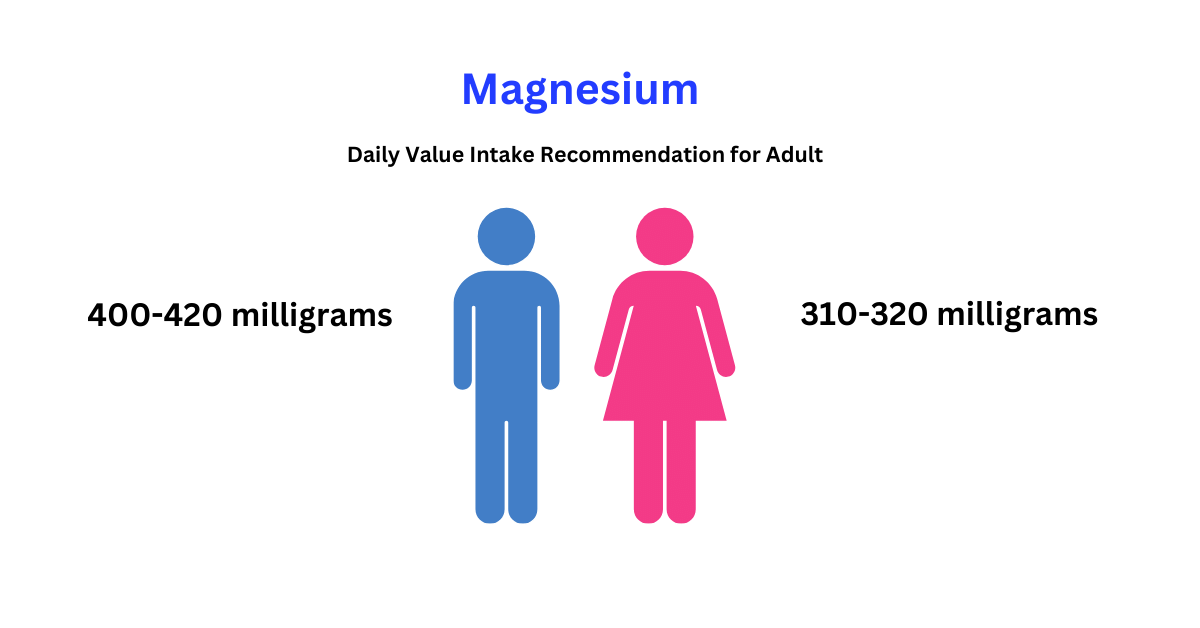
Meeting these recommended daily intakes ensures an adequate supply of magnesium (Adams et al., 2020).
Magnesium is found in various foods, with some being particularly rich sources.
Here are the top 10 high sources with necessary measurements of RDA:
- Almonds (1 ounce): Approximately 76 milligrams
- Cashews (1 ounce): Approximately 74 milligrams
- Spinach (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 78 milligrams
- Avocado (1 medium): Approximately 58 milligrams
- Black beans (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 60 milligrams
- Edamame (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 50 milligrams
- Whole wheat bread (2 slices): Approximately 46 milligrams
- Brown rice (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 42 milligrams
- Peanut butter (2 tablespoons): Approximately 49 milligrams
- Banana (1 medium): Approximately 32 milligrams
Including these foods in your diet helps ensure an adequate intake of magnesium.
Deficiencies and Supplementation
Magnesium deficiency can occur in individuals with certain gastrointestinal disorders or those with poor dietary choices.
● Magnesium deficiency can lead to muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, and weakness. It’s essential to maintain adequate magnesium levels, especially for individuals at risk of deficiency.
● In cases where individuals have difficulty obtaining enough magnesium from their diet or have specific medical conditions requiring higher magnesium intake, healthcare professionals may recommend magnesium supplements.
Interactions and Absorption
- Magnesium absorption can be influenced by factors such as calcium. High calcium intake can reduce magnesium absorption.
- Certain medications, such as diuretics and proton pump inhibitors, can also affect magnesium levels. Discussing potential interactions with healthcare providers is important for maintaining optimal magnesium levels.
- Adequate vitamin D intake is also essential for magnesium absorption in the intestines..
Conclusion
This magnesium guide has walked you through the crucial role that magnesium plays in maintaining health and vitality. It is clear that incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet is key to preventing deficiency and supporting bodily functions such as muscle and nerve operation, energy production, and protein synthesis. While deficiencies can be addressed through dietary adjustments and supplementation upon professional advice, understanding the interactions and absorption factors that impact magnesium levels is vital. Ultimately, following the insights and recommendations presented in this magnesium guide will contribute significantly to achieving and maintaining optimal health.