Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones, proper muscle function, and efficient nerve transmission. This article, your comprehensive Calcium Guide, aims to shed light on the importance of calcium, its dietary sources, the necessity of supplementation, and the factors affecting its absorption. Whether you’re looking to boost your bone health or ensure your body’s calcium needs are met, understanding the role of calcium is essential in this Calcium Guide.
Meeting Recommended Daily Intakes of Calcium
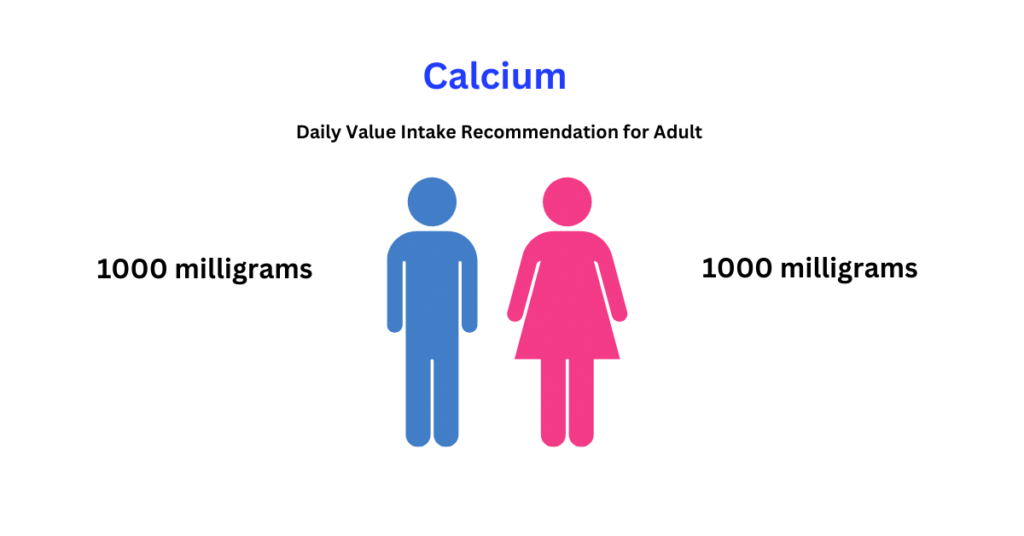
Meeting the recommended daily calcium intake is crucial to ensuring your body functions optimally. Adequate calcium supports bone density, muscle contraction, and nerve signaling. It’s particularly important for growing children, pregnant women, and older adults with higher mineral needs.
Top Calcium-Rich Food Sources
Incorporating foods high in calcium into your diet is a natural way to meet your daily requirements. Here are the top calcium sources and their respective measurements of RDA:
- Yogurt (1 cup): Approximately 300 milligrams
- Milk (1 cup): Approximately 300 milligrams
- Cheese (1 ounce): Approximately 200-300 milligrams
- Sardines (3 ounces, canned with bones): Approximately 325 milligrams
- Fortified plant-based milk (1 cup): Varies, check nutrition label
- Tofu (1/2 cup, prepared with calcium sulfate): Approximately 350-400 milligrams
- Collard greens (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 180 milligrams
- Spinach (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 120 milligrams
- Broccoli (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 31 milligrams
- Almonds (1 ounce): Approximately 76 milligrams
Including these calcium-rich foods in your diet can help ensure an adequate intake of this essential mineral.
Understanding Calcium Deficiency and Supplementation
Calcium deficiency concerns those with limited access to diverse diets, lactose intolerance, or certain medical conditions. This deficiency can lead to weakened bones, osteoporosis, and an increased risk of fractures [1]. To prevent these issues, healthcare professionals may recommend calcium supplements, particularly for people with risk factors of osteoporosis and those who struggle to meet their calcium needs through diet alone.
Interactions and Optimal Absorption of Calcium
Various factors can influence the absorption of this mineral. For example, high fiber intake may increase or decrease calcium absorption, depending on the type of fiber and the dose. Conversely, calcium absorption is enhanced when taken with Vitamin D. It’s crucial to discuss potential interactions and absorption strategies with healthcare providers to ensure you maintain optimal calcium levels for your health.
Conclusion: Embracing the Benefits of Calcium
Understanding the importance of calcium in your diet is key to maintaining strong bones and overall health. This Calcium Guide has provided you with the knowledge to include a variety of calcium sources in your diet and consider calcium supplements when necessary. Remember, a balanced approach to diet and supplementation, as outlined in this Calcium Guide, is the best way to harness the benefits of calcium for your body.