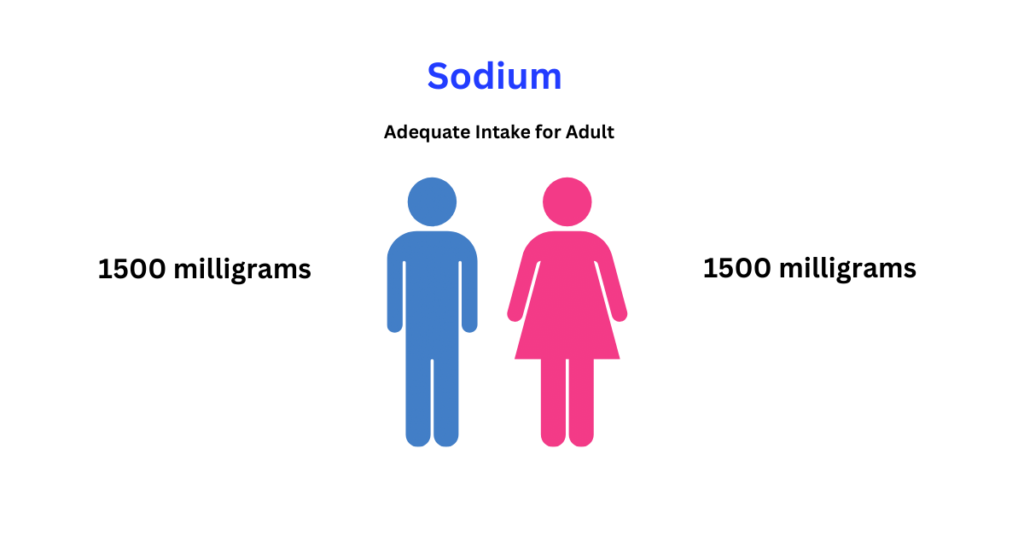
Sodium is a crucial mineral that our bodies require to function effectively. It plays a pivotal role in nerve signal transmission, muscle contraction, and fluid balance within our cells. However, managing sodium intake is a delicate dance, with too little or too much potentially leading to health complications. Understanding sodium deficiency symptoms, incorporating sodium-rich foods judiciously, and adhering to daily recommended sodium guidelines are fundamental steps toward maintaining your health.
Discovering Sodium-Rich Foods: A Balancing Act
Sodium isn’t just something you sprinkle on your meal from a salt shaker; it’s a mineral that’s part of many foods we eat, especially in packaged and restaurant foods. Here’s a rundown of where you might find sodium and how much you’re getting:
Common High-Sodium Foods and Their Content:
- Table salt: A teaspoon can pack around 2,325 milligrams of sodium.
- Canned soups: The sodium content can vary, so always peek at the label.
- Processed meats like bacon or ham: The sodium level differs, so it’s label-checking time.
- Cheese: The sodium content can change depending on the type, so check the label.
- Bread: One slice might have more sodium than you think, so looking at the nutritional info is best.
- Pizza: One slice can be quite high in sodium; the exact amount should be on the box or menu.
- Fast food items: Whether it’s a burger or fries, the sodium content is often listed on the menu or online.
- Pickles: A medium-sized pickle has about 382 milligrams of sodium.
- Cottage cheese: A cup offers around 918 milligrams of sodium.
- Soy sauce: A tablespoon contains about 879 milligrams of sodium.
Keeping track of your sodium intake is key, particularly in processed and fast foods, as they can easily push your sodium consumption over the edge.
Understanding Sodium Deficiency and Its Impact
Lack of enough sodium, while rare, can lead to sodium deficiency symptoms like headache, confusion, and fatigue. Ensuring adequate sodium levels is vital for overall health, especially in individuals who engage in high-intensity activities or are exposed to hot environments where they may lose more sodium through sweat.
Sometimes, especially when diet alone may not suffice or specific health conditions are at play, healthcare professionals may suggest sodium supplements.
The Interplay of Sodium and Health: Absorption Matters
The interrelationship between sodium and potassium in our bodies cannot be overstated. A low-sodium diet, coupled with high potassium intake, is often recommended for heart health and overall wellness.
- Sodium absorption can be affected by the amount of potassium consumed. A diet high in sodium can sometimes lead to increased potassium loss from the body.
- Certain medications might also alter sodium levels.
It is important to consult healthcare professionals to ensure you are maintaining optimal sodium levels.
You might be interested in: Vitamin B3 (Niacin): A Key Nutrient for Energy and Health
Conclusion
Sodium, a key element in our diets, is present in everything from a simple pinch of table salt to our favorite slice of pizza. While essential for bodily functions, the key to managing sodium intake effectively is finding the right balance and being aware of what we consume.
By keeping an eye on the sodium content in processed foods, fast food, and even in our home-cooked meals, which can include sodium-rich foods, we can avoid consuming too much and the associated health risks. The goal is to align our intake with the daily recommended sodium levels to support our body’s needs without excess. As we make our dietary choices, maintaining a careful balance with sodium-rich foods is crucial for long-term health and wellbeing.







