Step into the enriching world of Vitamin B3 (Niacin), a vital nutrient that energizes and sustains your overall health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the benefits of niacin (B3), explore a variety of vitamin B3-rich foods, and discuss the significance of niacin supplements. Ensuring you get enough niacin in your diet is crucial for your body’s energy production and well-being.
The Vital Role of Vitamin B3 in Your Diet
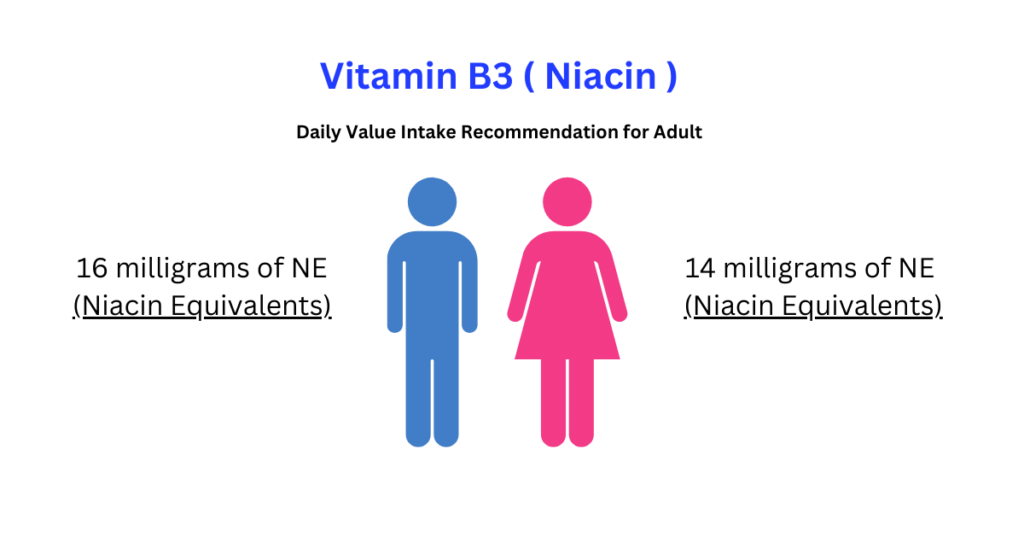
Niacin is a key component for maintaining health, energy production, and numerous physiological functions. Meeting the recommended daily intake is crucial for maintaining sufficient niacin levels.
Top Dietary Sources of Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
A diverse range of vitamin B3-rich foods ensures you get your daily dose of this essential nutrient:
- Chicken breast (3 ounces, cooked): Approximately 7.5 milligrams of NE
- Salmon (3 ounces, cooked): Approximately 8.6 milligrams of NE
- Tuna (3 ounces, cooked): Approximately 8.4 milligrams of NE
- Turkey (3 ounces, cooked): Approximately 6.7 milligrams of NE
- Peanuts (1 ounce): Approximately 4.2 milligrams of NE
- Sunflower seeds (1 ounce): Approximately 2 milligrams of NE
- Mushrooms (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 2 milligrams of NE
- Green peas (1/2 cup, cooked): Approximately 1.7 milligrams of NE
- Avocado (1 medium): Approximately 3.5 milligrams of NE
- Fortified cereals (1 serving): Check the nutrition label for amounts
Incorporating these niacin-rich foods into your diet can help ensure you meet your niacin requirements.
Recognizing and Addressing Vitamin B3 Deficiency
Niacin deficiency, known as pellagra, is relatively rare in modern diets but can still occur, particularly in cases of malnutrition or certain health conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders that impair nutrient absorption. The classic symptoms of pellagra, often summarized as the “three Ds,” include dermatitis (a scaly rash on skin exposed to sunlight), diarrhea, and dementia. These symptoms reflect the widespread impact of niacin deficiency on the body, including skin health, digestive function, and mental health.
The first step in addressing niacin deficiency is often dietary intervention, ensuring that foods high in vitamin B3 are included in the diet. Good sources include meat, fish, nuts, and certain vegetables. However, in cases where dietary adjustments aren’t sufficient or where medical conditions inhibit the absorption of niacin from food, vitamin B3 supplements can be an effective solution. Healthcare professionals might recommend niacin supplementation to quickly remedy the deficiency and prevent the serious consequences of prolonged pellagra.
Optimizing Vitamin B3 (Niacin) Absorption and Understanding Interactions
Various factors can influence the body’s ability to absorb and utilize niacin efficiently. For instance, a diet high in alcohol or certain medical conditions can impede niacin absorption, while at the same time, alcohol can also increase the body’s niacin requirements.
Niacin interacts significantly with other medications, notably cholesterol-lowering statins. While niacin can be beneficial in managing cholesterol levels, its combination with statins can increase the risk of muscle pain and potentially harmful muscle breakdown. This interaction underscores the importance of healthcare provider oversight when taking niacin supplements, especially for individuals already on statin therapy. Healthcare providers may adjust medication dosages or monitor for side effects to ensure niacin and statins’ safe and effective use.
Benefits of Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
The niacin benefits are broad and impactful. As an essential nutrient, niacin B3 is critical in converting food into energy. It’s involved in numerous metabolic processes and is essential for skin, nerves, and digestive system health.
- Heart Health: Niacin has been shown to improve cholesterol levels, reducing bad LDL cholesterol and increasing good HDL cholesterol, which is beneficial for heart health.
- Skin Health: Vitamin B3 helps maintain healthy skin and can be beneficial in treating various skin conditions, including acne and sun-damaged skin.
- Mental Health: Niacin plays a role in brain function and may positively impact mental health. Some research suggests niacin supplementation could support cognitive function and benefit individuals with certain mental health conditions.
- Digestive Function: Niacin helps convert food into usable energy and aids in the normal functioning of the digestive system.
- Nerve Health: Adequate niacin levels are important for nerve health, and a deficiency can lead to nerve damage and symptoms like tingling and numbness.
Conclusion
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) is indispensable in our health, from supporting energy production to maintaining healthy skin. By understanding the benefits of niacin, including a variety of niacin B3-rich foods in your diet, and considering supplements when necessary, you can ensure that your body receives all the niacin it needs to function optimally.