Vitamin D is essential for maintaining strong bones, supporting immune function, and contributing to overall well-being. This vitamin D guide provides a detailed exploration of calciferol’s crucial role in our health, highlighting its benefits, sources, and the importance of addressing deficiencies. Dive into the world of Vitamin D to understand how this key nutrient impacts your health and how you can optimize its levels for a healthier life.
Vitamin D: Essential for Bone Health and Beyond
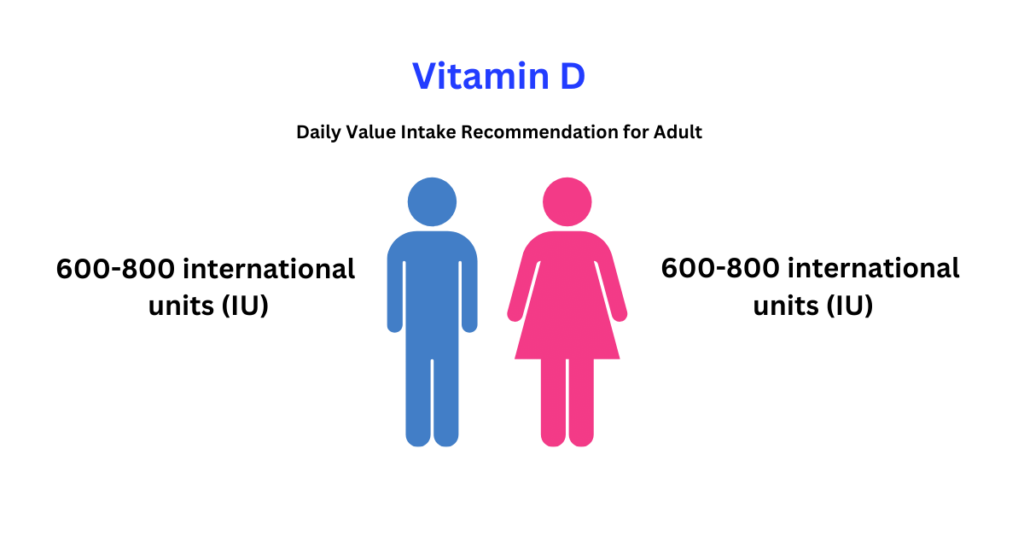
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining strong bones, supporting immune function, and contributing to overall health. Getting the recommended daily intake is essential for ensuring sufficient levels in the body.
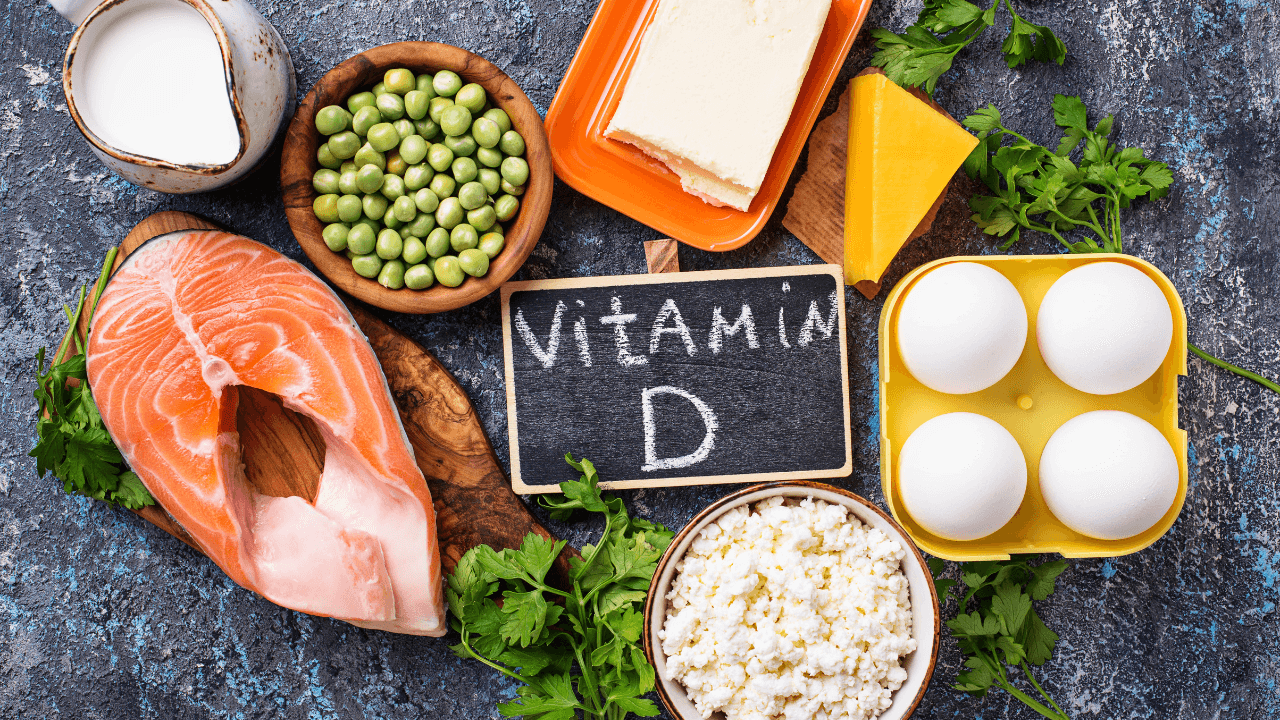
Top Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
While sunlight exposure is a primary source, several dietary options can boost your Vitamin D intake:
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel (3 ounces, cooked): Approximately 570-740 IU
- Cod liver oil (1 tablespoon): Approximately 1,360 IU
- Fortified milk (1 cup): Approximately 120 IU
- Fortified orange juice (1 cup): Approximately 100 IU
- Fortified cereals (1 serving): Check the nutrition label for amounts
- Eggs (1 large): Approximately 41 IU
- Cheese (1 ounce): Approximately 5 IU
- Beef liver (3 ounces, cooked): Approximately 42 IU
- Certain mushrooms like maitake and shiitake (1/2 cup, raw): Approximately 366-400 IU
Addressing Vitamin D Deficiency and the Role of Supplements
Vitamin D deficiency is a significant health concern, especially for individuals with limited sunlight exposure or inadequate dietary intake of this crucial vitamin. The deficiency can manifest in various ways, impacting different aspects of health. Among the most notable symptoms are weakened bones, which can lead to an increased risk of fractures. In children, a lack of Vitamin D can cause rickets, a condition marked by soft and weak bones, while in adults, it can lead to osteoporosis, characterized by porous and fragile bones.
Certain groups are at higher risk of Vitamin D deficiency, including those living in areas with limited sunlight, individuals with darker skin (as higher melanin levels reduce the skin’s ability to produce Vitamin D from sunlight), older people, and those with dietary restrictions that limit intake of Vitamin D-rich foods.
In response, healthcare professionals frequently recommend Vitamin D supplements to at-risk individuals. Supplements can provide a reliable source of Vitamin D, ensuring that the body receives an adequate amount to meet its needs. This is particularly important during the winter in northern latitudes with minimal sunlight.
Regular supplementation can help mitigate the risks associated with calciferol deficiency. However, it’s essential to consult with healthcare providers before starting any supplementation regimen, as they can offer guidance on the appropriate dosage based on individual health needs and circumstances.
Benefits of Vitamin D
The benefits of Vitamin D extend far beyond bone health, contributing to overall well-being in several ways:
1) Enhances Calcium Absorption:
Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption in the gut, essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
2) Immune System Support:
It plays a vital role in the functioning of the immune system and has been linked to a reduced risk of certain infections and immune-related disorders.
3) Mood Regulation:
Vitamin D is believed to play a role in regulating mood and reducing the risk of depression, especially seasonal depression, which can occur in areas with limited winter sunlight.
4) Reduces Inflammation and Supports Neurological Health:
Calciferol has anti-inflammatory properties and is thought to play a role in maintaining neurological health.
5) Heart Health:
Adequate Vitamin D levels have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease, as it may regulate blood pressure and prevent artery damage.
6) Muscle Strength:
It contributes to muscle strength, and its deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of muscle weakness and falls, particularly in older people.
Optimizing Vitamin D Absorption and Understanding Interactions
Being a fat-soluble vitamin, Vitamin D is best absorbed with dietary fats. Factors like obesity, gastrointestinal disorders, and certain medications can influence its absorption. It’s important to understand these aspects and consult healthcare providers to maintain optimal Vitamin D levels.
Conclusion:
This Vitamin D guide underscores the importance of Vitamin D in our diet and lifestyle. Vitamin D plays a crucial part in our well-being, from strengthening bones to enhancing immune function. By incorporating Vitamin D-rich foods and considering supplements when necessary, especially the Vitamin D3 and K2 combination, you can ensure your body receives the necessary support to thrive.







